![]()





Regulations Compliance for Shredding Services
___
Since 2004, Paper Cut's has provided professional expertise in document shredding, file storage, eWaste recycling, and hard-drive destruction procedures for your business to safeguard their records and data. Our specialized services ensure that your proprietary records are securely shredded to prevent unauthorized access to data related to your clients and business partners.
Our On-site mobile truck document shredding services provides affordable and convenient solutions especially useful for large companies and small businesses across Southern CA. We offer the most secure and affordable business integrated shredding and recycling services for organizations and businesses of all sizes across So Cal. What's more, 100% of your shredded records are destroyed and recycled, so they can be returned as post-consumer paper products in the future.
1. Maintaining Security Protocols —- Because document security is our business, we take the responsibility of enforcing data protection laws extremely seriously. By better monitoring our destruction and shredding processes, we ensure compliance to regulatory laws. This is in the best interest of both our company and our clients, since penalties for infringement can be severe and may include: fines, criminal charges and jail sentences, private rights of action, implementation of required security programs, and annual audits up to 20 years (consent decrees).
2. Enforcing Data-Protection Laws —- Why do we need to comply with all the State Legisltative Rulings and Federal Regulations? Because It's the law! Everyone must comply with mandatory California State and Federal Privacy Laws regarding document destruction and secured personal and financial data, as well as health, and medical records.
Our Compliance Team constantly reviews communications from the following Federal Government entities and agencies, including:
- Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
- Department of Justice (DOJ)
- Office of Civil Rights
- State Attorney General
- Consumer Financial Protection Board
3. Related Supreme Court Rulings —— The U.S. Supreme Court has ruled on many cases over the years related to identity theft issues, including privacy of information, and confidentiality of personal data. Specifically related to privacy, the Court ruled in "California vs. Greenwood" that "dumpster diving" is not illegal. Dumpster diving is the act of someone literally "diving" into a trash bin or dumpster sitting on the public street. It has become the predominate method of obtaining information by those involved in crimes related to identity theft, fraud, espionage and computer hacking.
4. Proper Regulatory Compliance —— Today, companies of all sizes are affected by privacy legislation and must take reasonable measures to protect against unauthorized access to confidential information. In addition, environmentally sound methods must be taken for destroying confidential documents to safeguard private information, maintain legislation compliance and avoid breach-of-security situations that might result in negative publicity. With trusted On-Site experience, and ISO certification to guarantee the highest standards in quality and service. Find out more about properly destroying confidential information and related regulations:
5. Applicable HIPAA Regulations —- There are legal reasons to ensure that your proprietary records are properly disposed. There are state and federal laws that make businesses liable for the protection of private information, whether legal or proprietary documents or otherwise. In fact, every law office and insurance business in the U.S. is required by law to protect confidential information and ensure that it is properly disposed of at the end of its lifecycle.
HIPAA, the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act identifies protected health information and sets rules for the security and privacy of this information. This 1996 law and the accompanying 2002 regulation known as the Privacy Rule restrict how health care providers may handle and disclose patient health information. In general, health care entities must ensure that only approved personnel handle protected health information and then only for purposes specified in the law and regulation.
6. Understanding Implications of FACTA —- Most relevant is the 2003 Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act (FACTA), an amendment to the Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) that was added, primarily, to protect consumers from identity theft. This federal legislation is aimed at the prevention and penalization of consumer fraud and identity theft. It mandates that any person who maintains or otherwise possesses or compiles consumer information for a business purpose must properly dispose of such information. That requires taking reasonable measures to protect against unauthorized access to or use of the information in connection with its disposal.
7. Implications of the 2005 FACTA Disposal Rule —- The Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act (2005 FACTA Disposal Rule Update) defines consumer information as personal identifying materials which extend beyond just a person’s name, including:
- a social security number
- a driver’s license number
- a phone number or e-mail address
- a physical address
To comply with the FACTA Disposal Rule, businesses and individuals must take reasonable measures to ensure such information does not fall into the wrong hands. Reasonable measures include the “burning, pulverizing, or shredding” of paper documents, such as the contracting of a third-party engaged in the document destruction business to dispose of confidential information in a manner consistent with the Act.
Failure to abide by FACTA may result in stiff penalties. Victims are entitled to actual damages sustained due to non-compliance; they may also seek statutory damages, and, in some cases, file class-action suits. Federal and state authorities are also empowered to bring legal enforcement actions against businesses that violate the Act.
8. Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act Compliance —- Following guidance of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA), enacted to protect private consumer information, the CA State Legislature passed Assembly Bill 2246 in January of 2001 with the following mandate:
"A business shall take all reasonable steps to destroy or arrange for the destruction of a customer's records within its custody or control containing personal information which is no longer to be retained by the business by (1) shredding (2) erasing, or (3)..."
9. FTC Red Flags Rule —- The Red Flags Rule helps fight identity theft. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC), the federal bank regulatory agencies, and the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) have issued regulations (the Red Flags Rule) requiring financial institutions and creditors to develop and implement written identity theft prevention programs.
As of May 1, 2009, companies must provide for the identification, detection and response to patterns, practices, or specific activities – known as “red flags” – that could indicate identity theft. Under the Red Flags Rule, financial institutions and creditors must develop a written program that identifies and detects the relevant warning signs of identity theft. The program must also describe appropriate responses that would prevent and mitigate the crime and detail a plan to update the program. Financial institutions and creditors must design and implement a program that is appropriate to their size and complexity, as well as the nature of their operations. As federal and state legislation tighten and affect not only financial and credit businesses across America, it is imperative that all organizations conduct due diligence and take appropriate measures to ensure end-of-lifecycle documentation is properly destroyed and recycled.
![]()
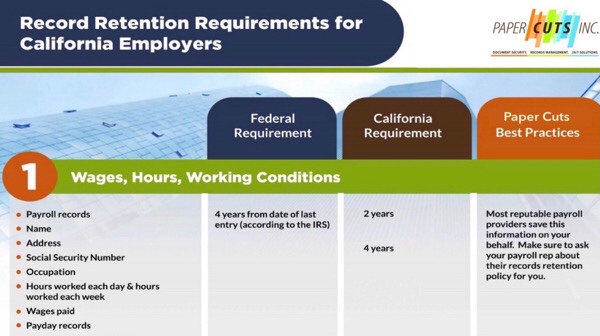
Records Retention Guide
___
We have put together an easy-to-follow guideline to assist you. This guideline covers a variety of records retention:
- Wages, Hours and Working Condition Records
- Occupational Safety and Health Records
- Non-discrimination and EEO Records
- Affirmative Action Records
- Worker’s Compensation Benefits
- Family and Medical Leaves
- Income Tax Records
- Unemployment Tax Records
- Social Security and Medicare Records
![]()
Affordable Paper Shredding in Compliance With Regulations
___
Paper Cuts offers the most secure, convenient, cost-effective and environmentally conscious solutions for ensuring proper disposal of confidential documents in compliance with state and federal regulations. Our secured process begins with our attentive staff working with you to develop a customized document shredding program that seamlessly fits your organization, 24/7. For daily paper flow, our top-of-the-line security consoles are strategically placed throughout your facility at no charge for convenient ongoing maintenance.
Since 2004, we have built our stellar reputation in compliance with state and federal laws for customer service and affordable rates because we understand that every business has unique requirements. We take great satisfaction in both our customized pricing and the thoroughness of our professional and confidential services. We will work with you to minimize document shredding or destruction costs for our integrated services in compliance with state and federal regulations. We offer a base fee and then we charge per container after that.
In many cases involving other companies that do NOT comply with state and federal regulations, vital business and personal information can be discovered just sitting amongst other trash disposed of in a public garbage bin near the same company business office, accessible to anyone walking by. Since most businesses have access to sensitive personal information, there is a growing body of legislation being supported to protect all citizens' confidentiality. Consequently, it is imperative that all confidential information, including but not limited to employee files, customer databases, reimbursements, supplier credentials, pricing data, revenue, manuscripts of proposals, and communications, be professionally and discreetly shredded by a trusted professional shredding firm like Paper Cuts.


![]()
Best Mobile Services in Compliance With Regulations
___
Paper Cut's mobile trucks equipped with advanced shredding technology are a key component of our document destruction business. These trucks are essential in differentiating our business from small in-house office shredders and large off-site shredding operations. Mobile shredding is the most secure and effective method for protecting our client’s confidential and private information.
Our secure process starts from the instant your employees deposit their confidential paper in our locked office consoles. Based on your service schedule, our Client Security Consultants will empty your containers and transport your sensitive information—in a locked wheeled tip cart—to the shredding truck parked outside.
Our On-Site Mobile shredding options provide are always in compliance with state and federal regulations with total flexibility and efficiency to benefit your budget and scheduling:
- Flexible shredding pick up schedules
- Value-added services like file indexing
- Document consoles eliminate in-office shredding
- Fax, e-mail, telephone, delivery services
- All-inclusive document management plans
- Unconditional storage satisfaction guarantee
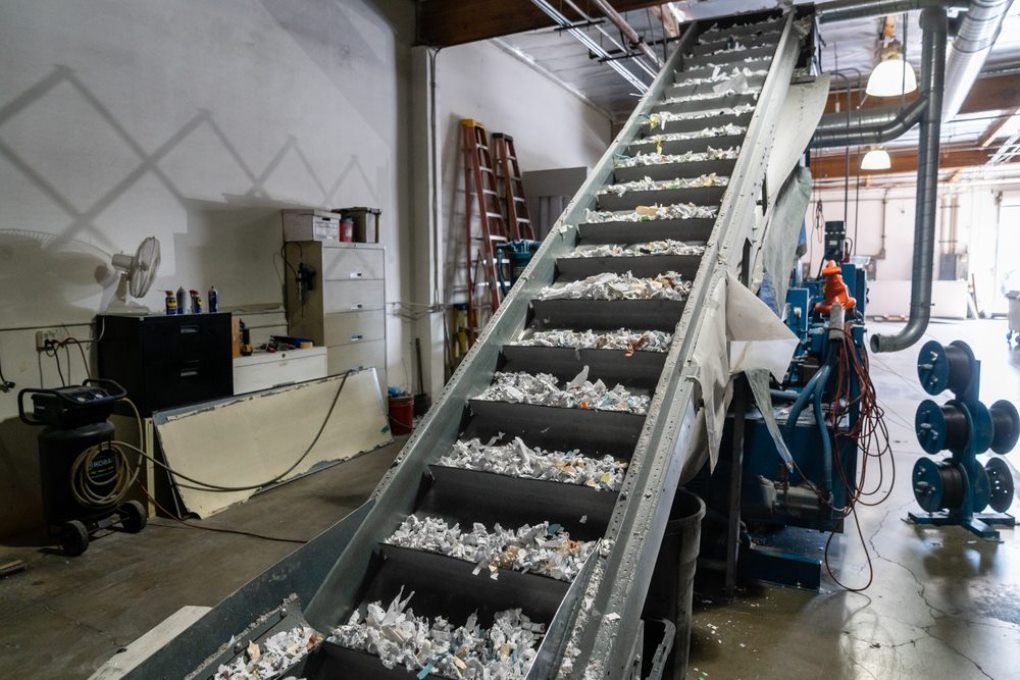
During the entire process, your paper is NEVER actually directly touched by the hand's of our Consultants. The wheeled tip cart is securely fastened to the chute of the shredding truck and automatically lifted inside the truck to shred your material into tiny pieces, which are mixed with other shredded paper that cannot be reconstructed.
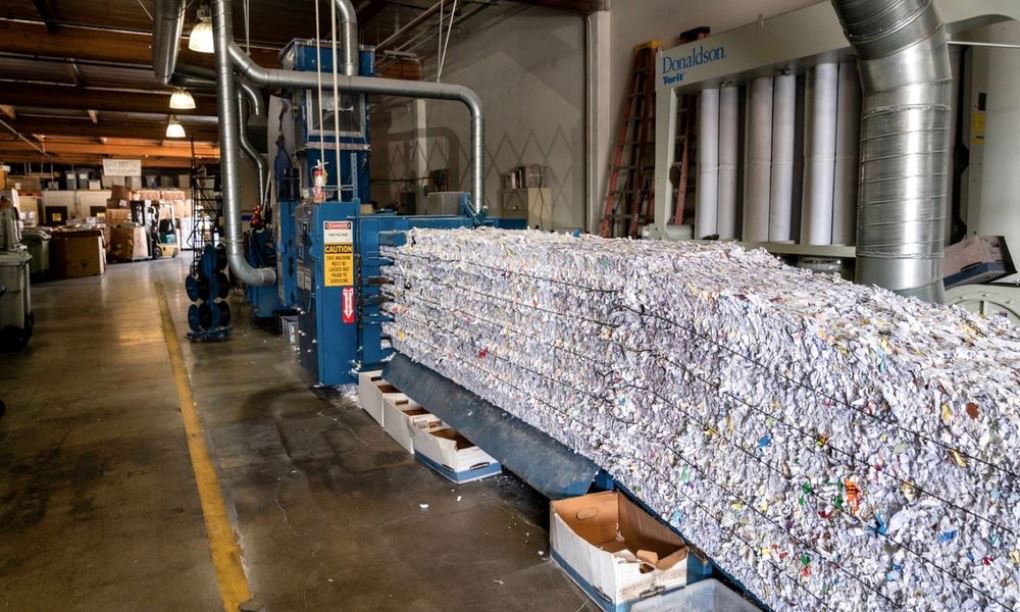


When you want to witness the destruction of your materials On-site or do not want un-destroyed materials leaving your premises, our experienced operators visit your location on a schedule that is best for you. Our specially-designed State-of-the-Art mobile shredding trucks can destroy up to 2 tons of paper per hour on the spot as you watch via closed circuit monitor on the truck to ensure the chain-of-custody during the entire process! This allows us to be in and out of your facilities quickly, ensuring all confidential documents have been securely destroyed. Our Client Service professionals never physically handle your documents, so the entire process is touch-free, adhering to strict security processes. This also provides you the opportunity to watch your items being destroyed at your place of business if you so choose.
![]()
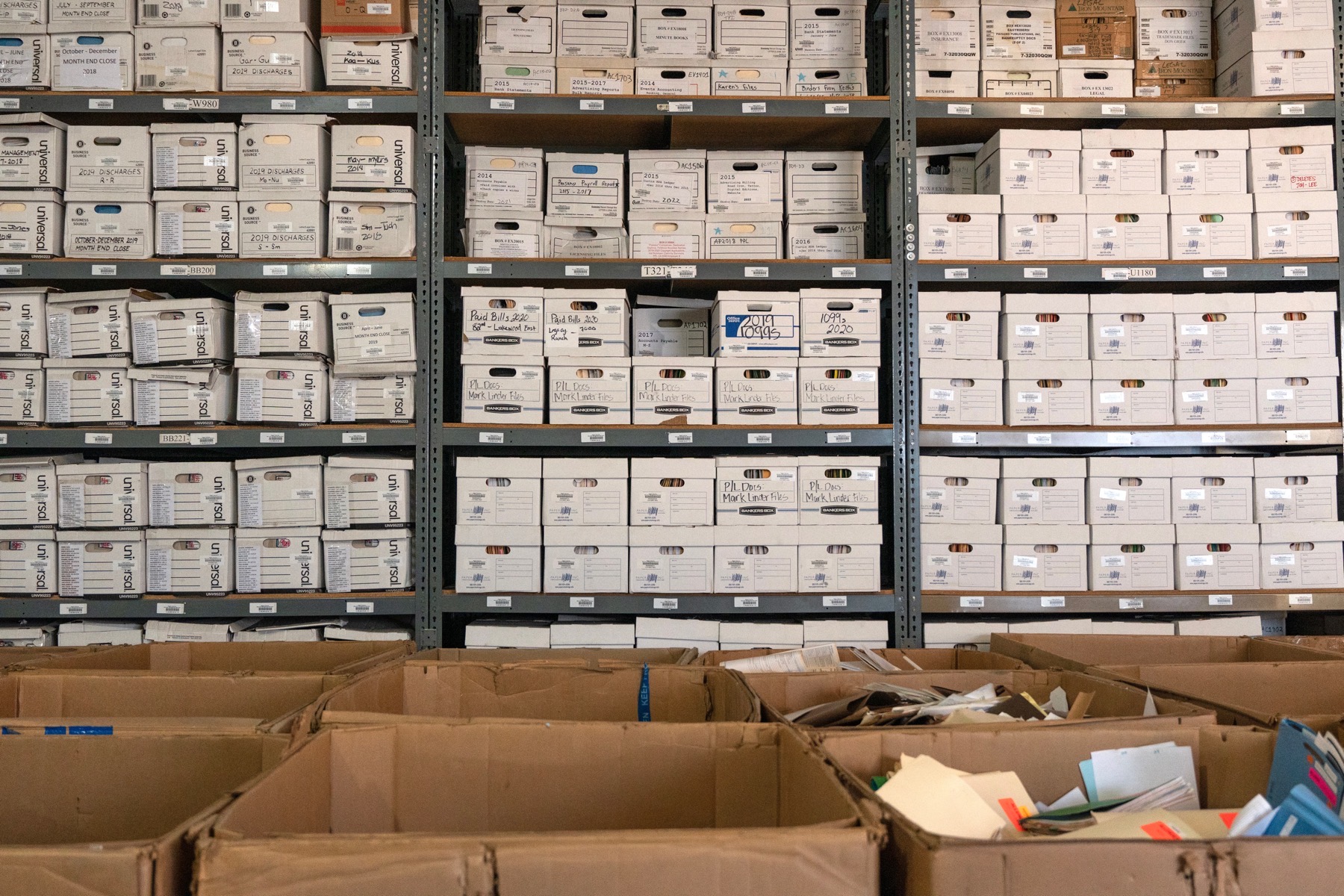
Superior File Storage and Records Management in Compliance With Regulations
___
Our custom file storage and records management solutions are always in compliance with state and federal regulations and are perfect for your long-term or short-term records storage, archiving, scanning, imaging, and consulting needs as your business grows. With our 24/7 around-the-clock access for attorneys and insurance organizations to your protected files, you always have easy retrieval of your paper records. You can also archive hard-copy records of any paper files scanned and have them sent to you electronically as needed. Need your paper document files picked up at your physical location in an emergency? No problem!
We consistently make sure our unique paper file storage or document shredding services are always compliant with state and federal regulations based in Southern CA. Because of this, we can customize a ’set it and forget it’ schedule for all of your comprehensive information security needs. Our plans are affordable and convenient to fit your specific budgetary needs whether you need one or any combination of our shredding, scanning, storage, recycling, destruction or file management services.

![]()
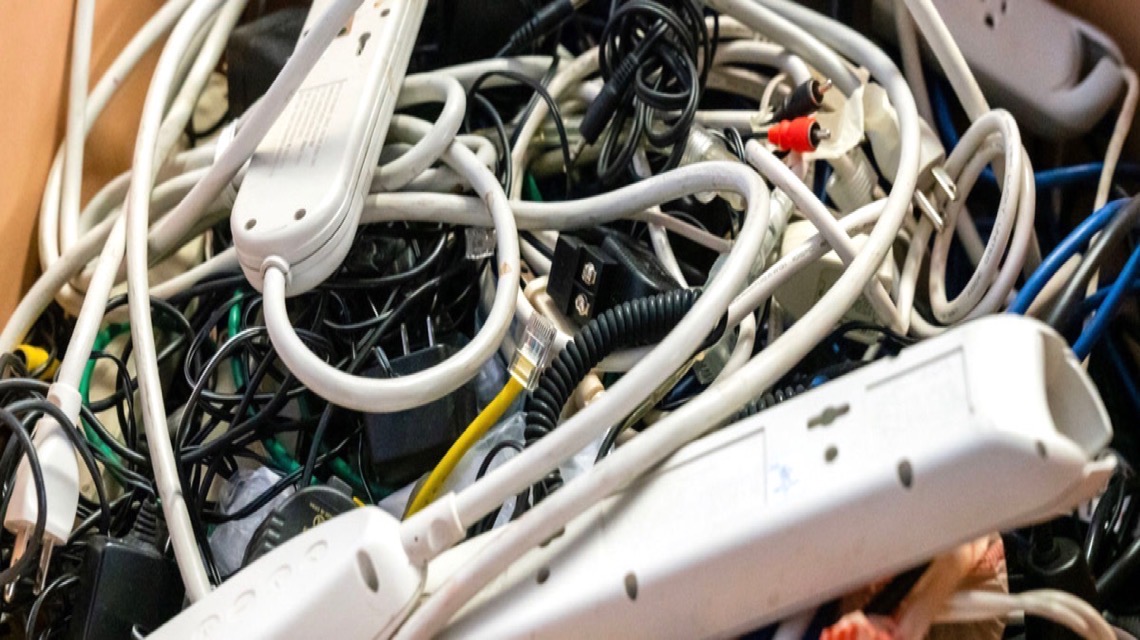
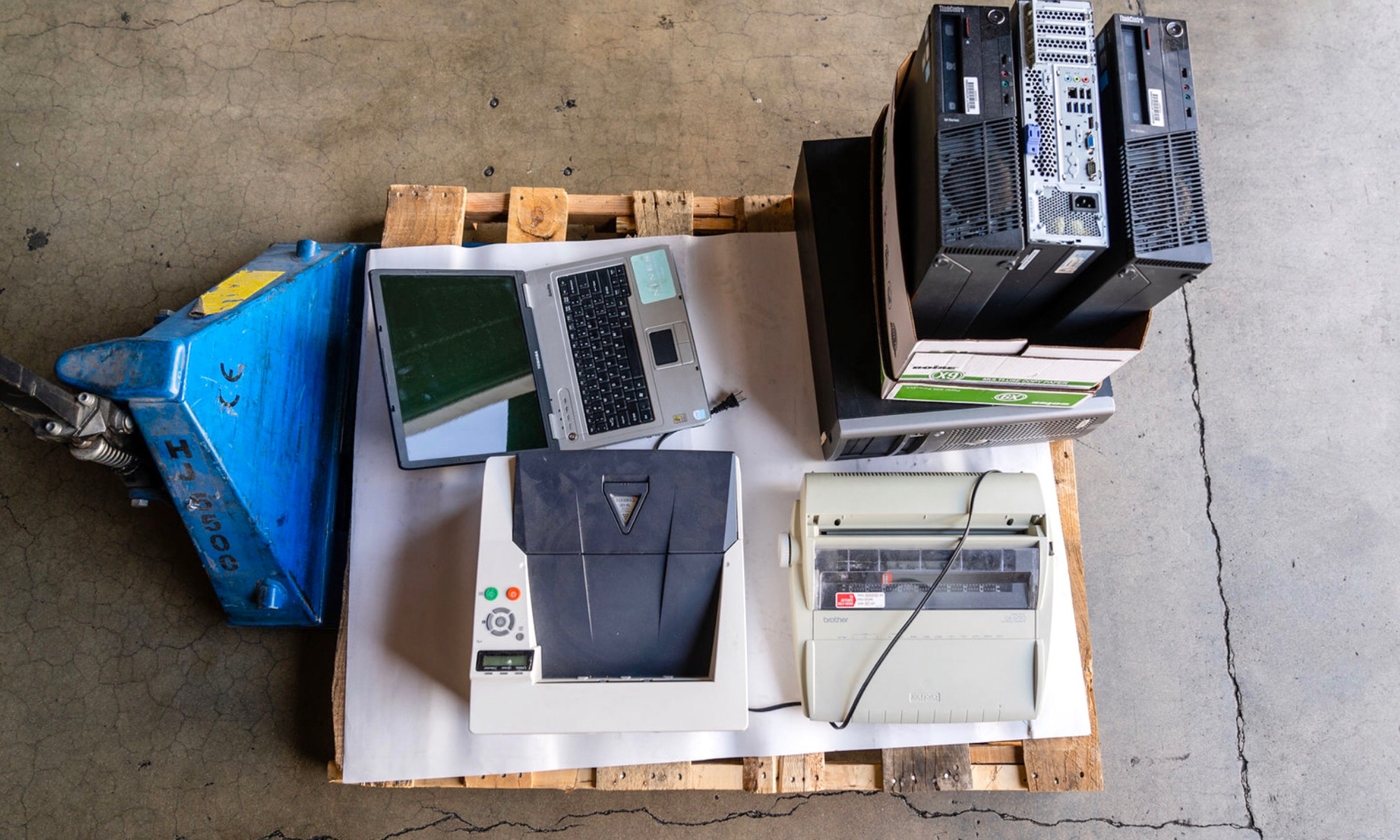
Convenient eWaste Disposal and Recycling Services
___
Old electronic devices, phones, fax machines, copiers, computers or hard-drives can hold valuable data inside, so we ensure total destruction of digital data in compliance with state and federal regulations by completely demolishing eWaste to tiny particles. Our eWaste disposal and recycling services for large law practices and insurance companies can take place in our off-site facility or conveniently at your location in your physical presence. Our shredding and destruction services are completely HIPAA and FACTA compliant. We guarantee all your confidential records are completed destroyed and provide you with a Certificate of Destruction to verify completion of your job.
Ensuring information security and asset protection is always in compliance with state and federal regulations is more crucial than ever in today's increasingly and fiercely competitive corporate world. Intellectual property kept digitally could fall into the hands of competitors, or fake goods could flood the market, and lawsuits could result from the misuse of sensitive customer and employee records.
To keep your company safe, you should put these things in a secure location and destroy them as soon as you are no longer required to keep them. Hard drives that are still functional can be accessed by those who need their data badly enough. Shredding the hard drive is the only foolproof method of erasing all data from it.
By contacting us, we avoid using degaussing devices and ensure no need for drilling holes. Except in cases where our client has made other arrangements, in compliance with state and federal laws all drives we receive from our customers are destroyed after two business days. Prior to destruction, a registration number list will be created for each drive and a copy of the list will be provided to you. Again, with each project, we will have a Certificate of Destruction issued to you.
In addition, whenever we destroy a disk drive for your business, we make sure to recycle it in full. Complete observance of all relevant privacy regulations, including HIPAA, is always maintained. We have the equipment capacity to destroy many devices at the same time. Our process is NAID approved and ensures the safest method of hard drive disposal.



![]()
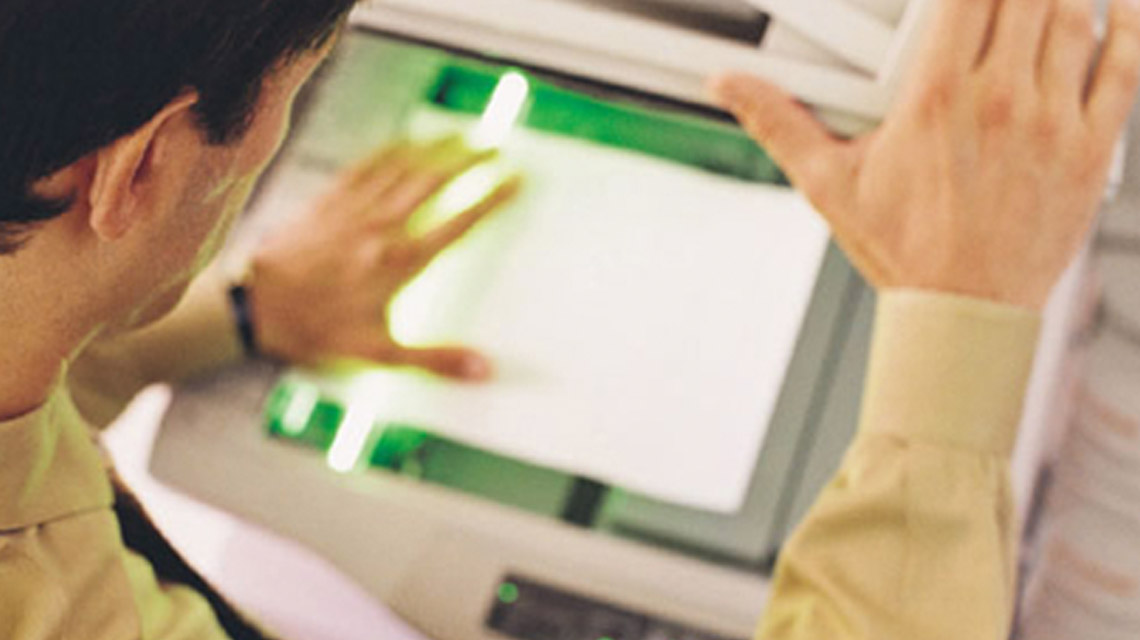

Efficient High-Speed Document Scanning
___
Paper Cuts offers custom High-Speed document scanning and imaging compliant with state and federal regulations to meet your specific personal or organizational needs. Our digital imaging service includes high-quality, large quantity copying, color scanning, and digital storage solutions. Your documents can be available for future retrieval purposes anytime on any digital device or computer in electronic formats including PDF, JPEG or TIFF files. This will save you time and money, as well as reduce your paper usage, physical file storage space and overall document management costs.
Our professional team of scanning experts is able to accommodate a wide variety of schedules and personalized needs for your law firms and insurance businesses, making it ideal for protecting large amounts of confidential documents. If you require service once a week, twice a week, every four weeks, or quarterly, we can facilitate a customized schedule for you. Customers have reported feeling safer while saving both time and money after switching to our professional document destruction services. You too can have ‘piece of mind’ when you make the right choice and let our team of certified destruction experts securely erase your private and sensitive data files.
![]()
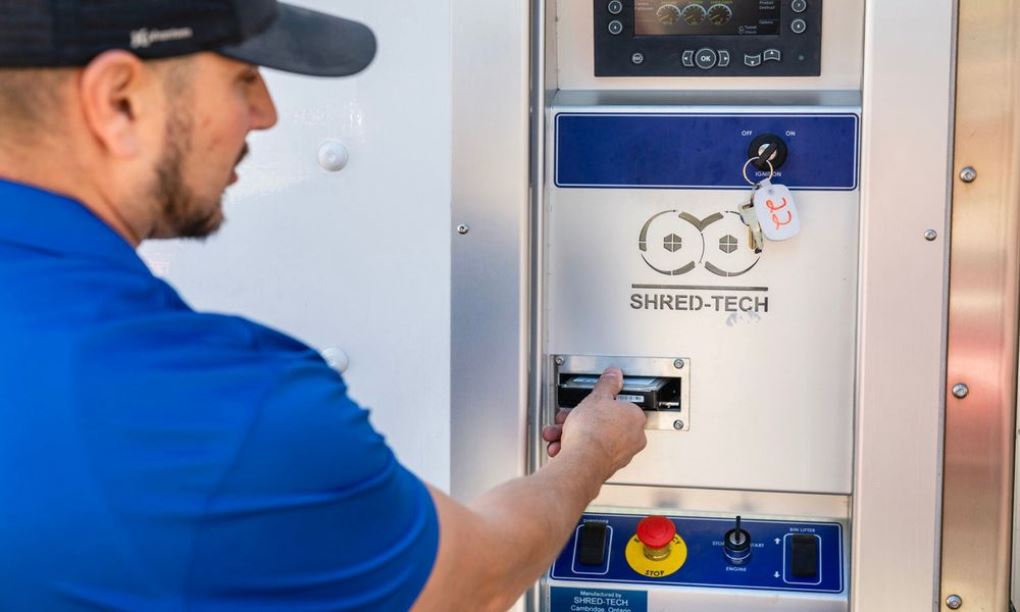

Effective Hard Drive and Data Disc Destruction
___
Paper Cuts securely destroys all types of hard-drives and data disc storage devices in compliance with state and federal regulations. Our certified destruction professionals can provide you with an efficient, cost-effective Off-site hard-drive destruction schedule. For better convenience, our mobile shredding trucks can stop by your location and destroy your drives and discs while you watch in front of you. In a hurry? You can always drop off your storage devices in person to be destroyed at our main San Fernando warehouse facility.
Plus, in addition to giving you the opportunity to watch your actual hard-drives being destroyed, we give you with a detailed Certificate of Destruction showing the date and the time of completion of destruction, whether it is OnSite at your location or OffSite at our main warehouse. Our goal is to always provide you with 100% Customer Satisfaction, guaranteed!
![]()
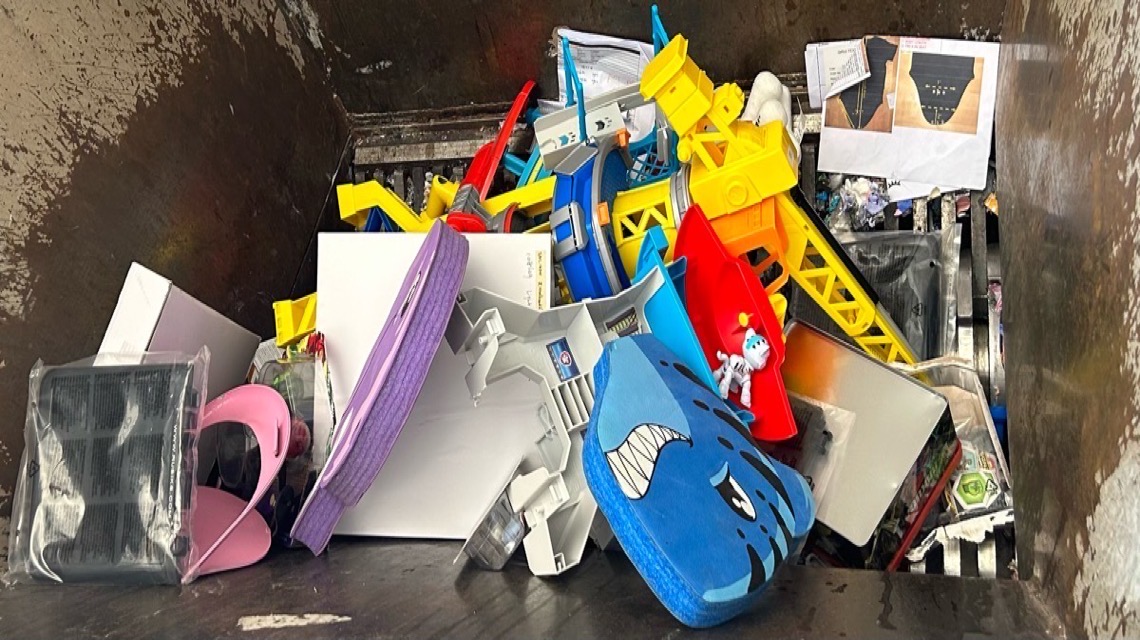
Best Product and Textiles Destruction Near Me
___
Paper Cuts is your go-to solution for superior product destruction and trademark protection compliant with state and federal regulations. Many of our customers routinely bring us broken or damaged items including clothes, toys, handbags, cosmetics, and packaging materials. Every year, we destroy thousands of distressed, and out-of-date products. Through our uniquely secured destruction processes, we can also discretely eliminate any counterfeit products that have you confiscated were illegally being sold.
Our Certified Destruction professionals will provide you with a strategic cost-effective Off-site resource for efficient product destruction, disposal and recycling service for unsaleable alcohol and non-alcohol products. We can also recover additional product materials including: Beverage products, Packaged materials, Unsaleable products, Counterfeit goods, as well as Liquid and Chemical products.

![]()
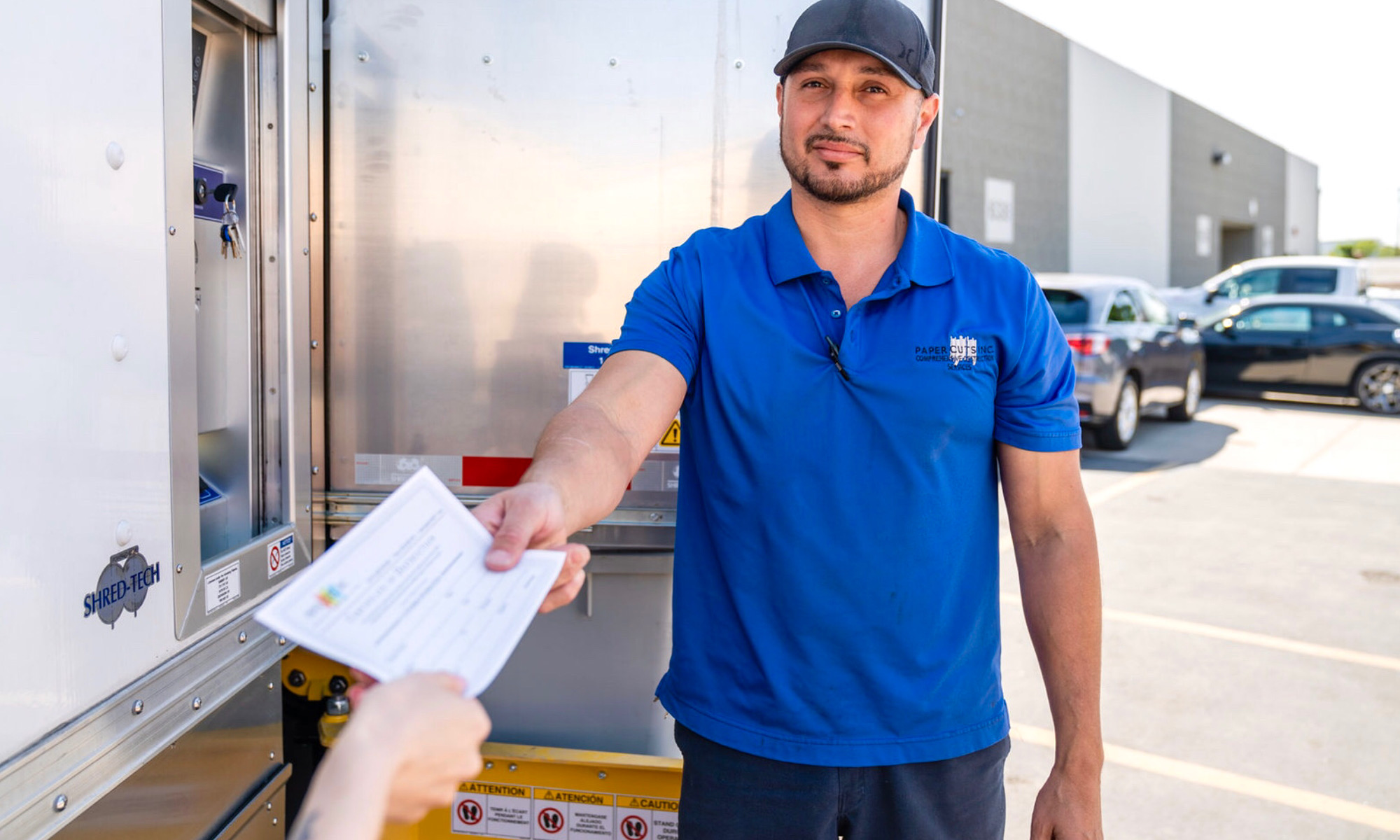
Certification of Document Destruction Guaranteed
___
Immediately following the completion of your professional document destruction, our team will issue you with a document shredding Certificate of Destruction. While the majority of competing document destruction services issue a Certificate of Destruction, ONLY Paper Cuts Document Shredding Services provides you with a Certificate of Destruction that specifically itemizes every secure destruction unit we maintained for you and the amount of material contained in each one.
In order to validate the Certificate of Destruction, both you and our Destruction Specialist in need to approve it. You will no longer have to worry about whether or not you are being overcharged or whether or not any of your bins were overlooked. All the legally required check-boxes have been ticked when you contact us for your document destruction and paper shredding services.


![]()